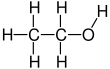
Bio ethanol
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈɛθənɒl/ | ||
|
Systematic IUPAC name
ethanol
|
|||
| Other names
Absolute alcohol
alcohol cologne spirit drinking alcohol ethylic alcohol EtOH ethyl alcohol ethyl hydrate ethyl hydroxide ethylol grain alcohol hydroxyethane methylcarbinol |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | B01253 | ||
| 1718733 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.526 | ||
| E number | E1510 (additional chemicals) | ||
| 787 | |||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C2H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 46.07 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.7893 g/cm3 (at 20 °C) | ||
| Melting point | −114.14 ± 0.03 °C (−173.45 ± 0.05 °F; 159.01 ± 0.03 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 78.24 ± 0.09 °C (172.83 ± 0.16 °F; 351.39 ± 0.09 K) | ||
| miscible | |||
| log P | −0.18 | ||
| Vapor pressure | 5.95 kPa (at 20 °C) | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 15.9 (H2O), 29.8 (DMSO) | ||
| −33.60·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
|
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.3611 | ||
| Viscosity | 1.2 mPa·s (at 20 °C), 1.074 mPa·s (at 25 °C) | ||
| 1.69 D | |||
| Related compounds | |||
|
Related compounds
|
Ethane Methanol |
||
| Supplementary data page | |||
|
Refractive index (n), Dielectric constant (εr), etc. |
|||
|
Thermodynamic
data |
Phase behaviour solid–liquid–gas |
||
| UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Ethanol, also called alcohol, ethyl alcohol, and drinking alcohol, is a chemical compound, a simple alcohol with the chemical formula C
2H
5OH. Its formula can be also written as CH
3−CH
2−OH or C
2H
5−OH (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group), and is often abbreviated as EtOH. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a slight characteristic odor. It is a psychoactive substance and is the principal type of alcohol found in alcoholic drinks.
Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes, and is most commonly consumed as a popular recreational drug. It also has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. The compound is widely used as a chemical solvent, either for scientific chemical testing or in synthesis of other organic compounds, and is a vital substance utilized across many different kinds of manufacturing industries. Ethanol is also used as a clean-burning fuel source.
...
Wikipedia