Binol
|
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
[1,1'-binaphthalene]-2,2'-diol
|
|||
| Other names
1,1'-bi-2-naphthol
1,1-binaphthol BINOL |
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
602-09-5 (R/S) 18531-94-7 ((R)-(+)) 18531-99-2 (S)-(−) |
|||
| 3D model (Jmol) |
Interactive image Interactive image |
||
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL138718 |
||
| ChemSpider |
11269 |
||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.104 | ||
| PubChem | 11762 | ||
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C20H14O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 286.32 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 205 to 211 °C (401 to 412 °F; 478 to 484 K) | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
1,1'-Bi-2-naphthol (BINOL) is an organic compound that is often used as a ligand for transition-metal catalysed asymmetric synthesis. BINOL has axial chirality and the two enantiomers can be readily separated and are stable toward racemisation. The specific rotation of the two enantiomers is +/- 35.5° (c=1 in THF). BINOL is a precursor for another chiral ligand called BINAP.
The organic synthesis of BINOL is not a challenge as such but the preparation of the individual enantiomers is.
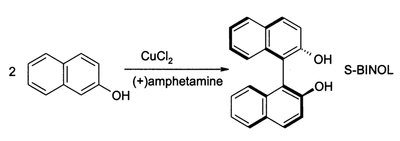
(S)-BINOL can be prepared directly from an asymmetric oxidative coupling of 2-naphthol with copper(II) chloride. The chiral ligand in this reaction is (S)-(+)-amphetamine.
Racemic BINOL can also be produced using iron(III) chloride as an oxidant. The mechanism involves complexation of iron(III) into the hydroxyl, followed by a radical coupling reaction of the naphthol rings initiated by iron(III) reducing into iron(II).
...
Wikipedia