Biloxi language
| Biloxi | |
|---|---|
| Tanêksąyaa ade | |
| Native to | United States |
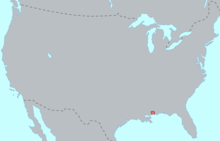
| Region | Mississippi, Louisiana |
| Extinct | 1930s, with the death of Emma Jackson |
|
Siouan
|
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | |
| Glottolog | bilo1248 |
 |
|
Biloxi is an extinct Siouan language which was at one time spoken by the Biloxi tribe living in present-day Mississippi, Louisiana, and southeast Texas.
The Biloxi first encountered Europeans in 1699 along the Pascagoula River. By the mid-18th century, they had settled in central Louisiana. Some were also noted in Texas in the early 19th century.
By the early 19th century, their numbers were already dwindling. By 1934, the last native speaker, Emma Jackson, was in her 80s.Morris Swadesh and Mary Haas spoke with Emma Jackson in 1934 and confirmed her status as a speaker of the language.
Biloxi is an Ohio Valley, or Southeastern Siouan language related to Ofo and Tutelo.
Multiple possible inventories have been suggested; this article follows that of Einaudi (1976).
Along with contrastive nasalization, Biloxi also had phonemic vowel length.
Phonetic notes:
Dorsey & Swanton (1912) postulated phonemic vowel length. This was verified by Haas and Swadesh in speaking with Emma Jackson in 1934, their findings appearing in Haas (1968).
Also, there may still be some uncertainty as to whether certain words contain /ą/ or /an/.
Phonetic notes:
Biloxi may also have had a phonemic aspiration distinction for some segments.
Syllable structure is (C)(C)(C)V(C) or (C)V(C)(C). However, clusters of three consonants are rare.
Most words end in a vowel. Ones which don't usually end in /k/ or /x/ as a result of deletion, e.g. tox from toho 'he fell'.
Consonant clusters usually don't end syllables. When they do, it's probably caused by vowel deletion, e.g. tohoxk from tohoxka 'horse'.
The following consonant clusters are observed:
It may be noted that geminates do not occur, besides /n/ sonorants and probably /d/ only occur as the second elements of clusters, /h/ and /m/ are never the second element, and fricatives do not co-occur.
There are a few three-consonant clusters, all of the form C+s+stop or C+x+glide and some with alternate forms:
There are many verb roots and two mode markers with the morphophonemically conditioned alternation e~a~i (underlying ||E||). Included in them are:
...
Wikipedia
