Beta-binomial distribution
|
Probability mass function
|
|
|
Cumulative distribution function

|
|
| Parameters |
n ∈ N0 — number of trials (real) (real) |
|---|---|
| Support | k ∈ { 0, …, n } |
| pmf | |
| CDF |
where 3F2(a,b,k) is the generalized hypergeometric function =3F2(1, α + k + 1, −n + k + 1; k + 2, −β − n + k + 2; 1) |
| Mean | |
| Variance | |
| Skewness | |
| Ex. kurtosis | See text |
| MGF |
|
| CF |
|
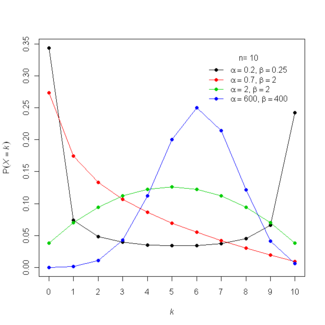
In probability theory and statistics, the beta-binomial distribution is a family of discrete probability distributions on a finite support of non-negative integers arising when the probability of success in each of a fixed or known number of Bernoulli trials is either unknown or random. The beta-binomial distribution is the binomial distribution in which the probability of success at each trial is not fixed but random and follows the beta distribution. It is frequently used in Bayesian statistics, empirical Bayes methods and classical statistics to capture overdispersion in binomial type distributed data.
It reduces to the Bernoulli distribution as a special case when n = 1. For α = β = 1, it is the discrete uniform distribution from 0 to n. It also approximates the binomial distribution arbitrarily well for large α and β. The beta-binomial is a one-dimensional version of the Dirichlet-multinomial distribution, as the binomial and beta distributions are univariate versions of the multinomial and Dirichlet distributions, respectively.
The Beta distribution is a conjugate distribution of the binomial distribution. This fact leads to an analytically tractable compound distribution where one can think of the parameter in the binomial distribution as being randomly drawn from a beta distribution. Namely, if
...
Wikipedia












