Beta-Hydroxy beta-methylbutyric acid
 |
|
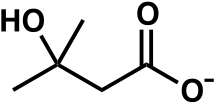
Top: β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid
Bottom: β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyrate |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth or nasogastric |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolites | HMB-CoA, HMG-CoA, mevalonate, cholesterol, acetoacetyl-CoA, acetyl-CoA |
| Onset of action |
HMB-FA: 30–60 minutes HMB-Ca: 1–2 hours |
| Biological half-life |
HMB-FA: 3 hours HMB-Ca: 2.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (10–40% excreted) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms |
Conjugate acid form: β-hydroxyisovaleric acid 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid Conjugate base form: hydroxymethylbutyrate |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.128.078 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C5H10O3 |
| Molar mass | 118.131 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Density | ~1.1 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| Melting point | −80 °C (−112 °F) (glass) |
| Boiling point | 128 °C (262 °F) at 7 mmHg |
|
|
|
|
β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid (HMB), also known as β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate, is a naturally produced substance in humans that is used as dietary supplement and as an ingredient in some medical food products. HMB can reduce the loss of lean body mass in individuals experiencing age-related muscle loss, but more research is needed to determine how it affects muscle strength and function in older adults. In healthy adults, supplementation with HMB has been shown to increase gains in muscle size, muscle strength, lean body mass, reduce skeletal muscle damage, and speed recovery from exercise. HMB produces these effects in part by stimulating the production of proteins and inhibiting the breakdown of proteins in muscle tissue.Medical reviews have found no issues with safety from long-term use as a dietary supplement in adults.
HMB is a metabolite of L-leucine that is produced in the body through oxidation of the ketoacid of L-leucine (α-ketoisocaproic acid). Since only a small fraction of L-leucine is metabolized into HMB, pharmacologically active concentrations of the compound in blood and muscle can only be achieved by supplementing HMB directly. A healthy adult produces approximately 0.3 grams per day, while supplemental HMB is usually taken in doses of 3–6 grams per day. HMB is sold worldwide as a dietary supplement at a cost of about US$30–50 per month when taking 3 grams per day. HMB is also contained in several nutritional products, including certain formulations of Ensure, Juven, and Myoplex. Small amounts of HMB are present in certain foods, such as alfalfa, asparagus, avocados, cauliflower, grapefruit, catfish, and milk.
...
Wikipedia
