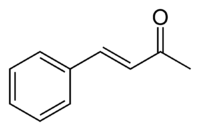
Benzylideneacetone
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
(E)-4-Phenylbut-3-ene-2-one
|
|
| Other names
Benzalacetone
Benzylideneacetone Methyl styryl ketone Benzylidene acetone |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.142 |
| EC Number | 204-555-1 (trans) |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number | EN0330000 |
| UNII |
|
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H10O | |
| Molar mass | 146.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | pale yellow solid |
| Density | 1.008 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 39 to 42 °C (102 to 108 °F; 312 to 315 K) |
| Boiling point | 260 to 262 °C (500 to 504 °F; 533 to 535 K) |
| 1.3 g/L | |
| Solubility in other solvents | nonpolar solvents |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | irritant |
| GHS pictograms |  |
| GHS signal word | Warning |
| H315, H317, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P272, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362 | |
| Flash point | 116 °C (241 °F; 389 K) |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Dibenzylideneacetone cinnamaldehyde |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Benzylideneacetone is the organic compound described by the formula C6H5CH=CHC(O)CH3. Although both cis- and trans-isomers are possible for the α,β-unsaturated ketone, only the trans isomer is observed. Its original preparation demonstrated the scope of condensation reactions to construct new, complex organic compounds. Benzylideneacetone is used as a flavouring ingredient in food and perfumes.
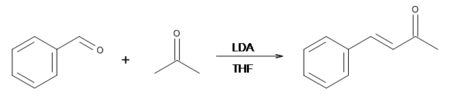
Benzylideneacetone can be efficiently prepared by the NaOH-induced condensation of the readily available reagents acetone and benzaldehyde:
However, the benzylideneacetone formed via this reaction can undergo another Claisen-Schmidt condensation with another molecule of benzaldehyde to form dibenzylideneacetone. Because relatively weak bases such as NaOH make very little of the enolate ion at equilibrium, there is still a lot of unreacted base left in the reaction mixture, which can go on and remove protons from the alpha carbon of benzylideneacetone, allowing it to undergo another Claisen-Schmidt condensation and make dibenzylideneacetone.
If, on the other hand, lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is used as the base, all of the acetone will deprotonated, making enolate ion quantitatively. Therefore, the most efficient way to make benzylideneacetone is to use equimolar amounts of LDA, acetone, and benzaldehyde. Because LDA is an extremely strong base, the reaction must be done in an inert solvent, such as THF or ether.
...
Wikipedia