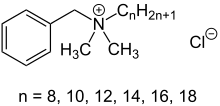
Benzalkonium chloride
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
N-Alkyl-N-benzyl-N,N-dimethylammonium chloride; Alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride; ADBAC; BC50 BC80; Quaternary ammonium compounds; quats
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
8001-54-5 |
|
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:3020 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL502109 |
| ChemSpider |
D09AA11 ([http://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/?code=D09AA11 WHO) (dressing), R02AA16 (WHO).html none D09AA11 (WHO) (dressing), R02AA16 (WHO)] |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.058.301 |
| EC Number | 264-151-6 |
| KEGG |
D00857 |
| RTECS number | BO3150000 |
| UNII |
F5UM2KM3W7 |
| Properties | |
| variable | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Appearance | 100% is white or yellow powder; gelatinous lumps; Solutions BC50 (50%) & BC80 (80%) are colorless to pale yellow solutions |
| Density | 0.98 g/cm3 |
| very soluble | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D08AJ01 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
|
EU classification (DSD)
|
C, N |
| R-phrases | R21/22, R34, R50 |
| S-phrases | (S2), S36/37/39, S45, S61 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) (if solvent based) |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Benzalkonium chloride, also known as BZK, BKC, BAC, alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride and ADBAC, is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. It has three main categories of use: as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and as a phase transfer agent. ADBACs are a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides, in which the alkyl group has various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths.
Depending on purity, benzalkonium chloride ranges from colourless to a pale yellow (impure). Benzalkonium chloride is readily soluble in ethanol and acetone. Although dissolution in water is slow, aqueous solutions are easier to handle and are preferred. Aqueous solutions should be neutral to slightly alkaline. Solutions foam when shaken. Concentrated solutions have a bitter taste and a faint almond-like odour.
Standard concentrates are manufactured as 50% and 80% w/w solutions, and sold under trade names such as BC50, BC80, BAC50, BAC80, etc. The 50% solution is purely aqueous, while more concentrated solutions require incorporation of rheology modifiers (alcohols, polyethylene glycols, etc.) to prevent increases in viscosity or gel formation under low temperature conditions.
Benzalkonium chloride also possesses surfactant properties, dissolving the lipid phase of the tear film and increasing drug penetration, making it a useful excipient.
Benzalkonium chloride is a mainstay of phase-transfer catalysis, an important technology in the synthesis of organic compounds, including drugs.
Especially for their antimicrobial activity, benzalkonium chloride is an active ingredient in many consumer products:
Benzalkonium chloride is also used in many non-consumer processes and products, including as an active ingredient in surgical disinfection. A comprehensive list of uses includes industrial applications. An advantage of benzalkonium chloride, not shared by ethanol-based antiseptics or hydrogen peroxide antiseptic, is that it does not cause a burning sensation when applied to broken skin.,
...
Wikipedia

