Bcl-2 family
| Apoptosis regulator proteins, Bcl-2 family | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
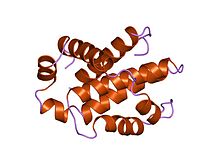
Structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death.
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Bcl-2 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00452 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000712 | ||||||||
| SMART | SM00337 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00829 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 1maz | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 1maz | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 42 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 2l5b | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
The Bcl-2 Family (TC# 1.A.21) consists of a number of evolutionarily-conserved proteins that share Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains. The Bcl-2 family is most notable for their regulation of apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, at the . The Bcl-2 family proteins consists of members that either promote or inhibit apoptosis, and control apoptosis by governing mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). There are a total of 25 genes in the Bcl-2 family known to date.
Bcl-2 family proteins have a general structure that consists of a hydrophobic α-helix surrounded by amphipathic α-helices. Some members of the family have transmembrane domains at their c-terminus which primarily function to localize them to the mitochondrion.
Bcl-x(L) is 233 amino acyl residues (aas) long and exhibits a single very hydrophobic putative transmembrane α-helical segment (residues 210-226) when in the membrane. Homologues of Bcl-x include the Bax (rat; 192 aas) and Bak (mouse; 208 aas) proteins, which also influence apoptosis. The high resolution structure of the monomeric soluble form of human Bcl-x(L) has been determined by both x-ray crystallography and NMR.
The structure consists of two central primarily hydrophobic α-helices surrounded by amphipathic helices. The arrangement of the α-helices in Bcl-X(L) resembles that for diphtheria toxin and the colicins. Diphtheria toxin forms a transmembrane pore and translocates the toxic catalytic domain into the animal cell cytoplasm. The colicins similarly form pores in lipid bilayers. Structural homology therefore suggests that Bcl-2 family members that contain the BH1 and BH2 domains (Bcl-X(L) Bcl-2 and Bax) function similarly.
The members of the Bcl-2 family share one or more of the four characteristic domains of homology entitled the Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains (named BH1, BH2, BH3 and BH4) (see figure). The BH domains are known to be crucial for function, as deletion of these domains via molecular cloning affects survival/apoptosis rates. The anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins, such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, conserve all four BH domains. The BH domains also serve to subdivide the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins into those with several BH domains (e.g. Bax and Bak) or those proteins that have only the BH3 domain (e.g. Bim Bid and BAD).
...
Wikipedia
