Azygos veins
| Azygos vein | |
|---|---|

Superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, azygos vein and their tributaries. (Vena azygos labeled at center.)
|
|
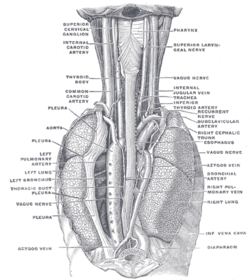
POSTERIOR VIEW: The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum. Seen from behind. (Azygos vein labeled at bottom left.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | Right supracardinal vein |
| Source | superior intercostal vein |
| Drains to | superior vena cava |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena azygos |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.106 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
v_05/12849551 |
| TA | A12.3.07.001 |
| FMA | 4838 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The azygos vein is a vein running up the side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blood to the right atrium when either of the venae cavae is blocked.
The azygos vein transports deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen into the superior vena cava vein. The anatomy of this blood vessel can be quite variable. In some rare variations for example, it also drains thoracic veins, bronchial veins and even gonadal veins. The vein is so named because it has no symmetrically equivalent vein on the left side of the body.
It is formed by the union of the ascending lumbar veins with the right subcostal veins at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra, ascending in the posterior mediastinum, and arching over the right main bronchus posteriorly at the root of the right lung to join the superior vena cava. This "arch of the azygos vein" (arcus venae azygos) is an important anatomic landmark. As an anatomical variation in 1-2% of the population, the arch can be displaced laterally, thereby creating a pleural septum separating an azygos lobe from the upper lobe of the right lung.
A major tributary is the hemiazygos vein, a similar structure on the opposite side of the vertebral column. Other tributaries include the bronchial veins, pericardial veins, and posterior right intercostal veins. It communicates with the vertebrael venous plexuses.
...
Wikipedia
