Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1
| Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 | |
|---|---|
 |
|
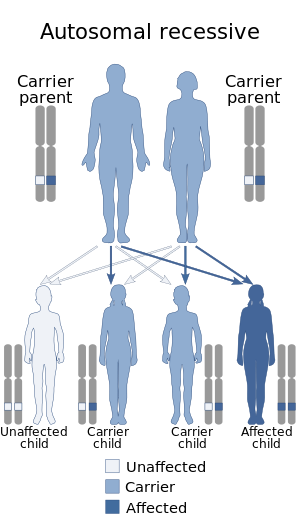
| Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 is autosomal recessive | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | endocrinology |
| ICD-10 | E31.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 258.1 |
| OMIM | 240300 |
| DiseasesDB | 29212 |
| eMedicine | med/1867 |
| MeSH | D016884 |
| Orphanet | 3453 |
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1), also known as autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis–ectodermal dystrophy/dysplasia (APECED), autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1, Whitaker syndrome, or candidiasis-hypoparathyroidism–Addison's disease syndrome, is a subtype of autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome (autoimmune polyglandular syndrome) in which multiple endocrine glands dysfunction as a result of autoimmunity. It is a genetic disorder inherited in autosomal recessive fashion due to a defect in the AIRE gene (autoimmune regulator), which is located on chromosome 21 and normally confers immune tolerance.
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 symptoms and signs include the following:
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 is a condition caused in an autosomal recessive manner.Furthermore, it is due to a defect in AIRE gene(which helps to make a protein that is called the autoimmune regulator) mapped to 21q22.3 chromosome location, hence chromosome 21
In autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 mechanism one finds that the maintenance of immunological tolerance plays a role Furthermore upon looking at the AIRE gene,one finds at least 90 mutations in the gene, in those affected with this condition.
Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 mechanism also indicates that affected individuals autoantibodies have considerable reactions with both interferon-omega and interferon alpha.
In terms of diagnosis for this condition, the following methods/tests are available:
...
Wikipedia
