Arytenoid cartilage
| Arytenoid cartilage | |
|---|---|
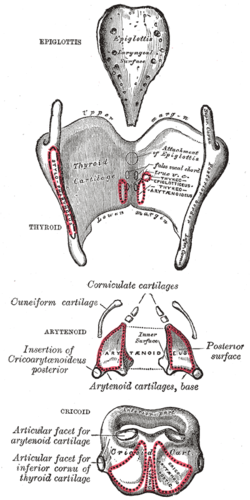
The cartilages of the larynx seen from behind
|
|
| Details | |
| Precursor | 4th and 6th branchial arch |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cartilagines arytaenoideae |
| MeSH | A02.165.507.083 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
c_12/12217087 |
| TA | A06.2.04.001 |
| FMA | 55109 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The arytenoid (/ærᵻˈtiːnɔɪd/) cartilages are a pair of small three-sided pyramids which form part of the larynx, to which the vocal folds (vocal cords) are attached. These allow and aid in the vocal cords' movement.
Each is pyramidal or -shaped in form (arytenoid comes from Greek arytaina meaning ladle + eidos, meaning form), and has three surfaces, a base, and an apex.
The posterior surface is a triangular, smooth, concave, and gives attachment to the Arytænoidei obliquus and transversus.
The antero-lateral surface is somewhat convex and rough. On it, near the apex of the cartilage, is a rounded elevation (colliculus) from which a ridge (crista arcuata) curves at first backward and then downward and forward to the vocal process. The lower part of this crest intervenes between two depressions or foveæ, an upper, triangular, and a lower oblong in shape; the latter gives attachment to the Vocalis muscle.
The medial surface is narrow, smooth, and flattened, covered by mucous membrane, and forms the lateral boundary of the intercartilaginous part of the rima glottidis.
The base of each cartilage is broad, and on it is a concave smooth surface, for articulation with the cricoid cartilage.
The apex of each cartilage is pointed, curved backward and medialward, and surmounted by a small conical, cartilaginous nodule, the corniculate cartilage.
They allow the vocal folds to be tensed, relaxed, or approximated.
...
Wikipedia
