Artery of Percheron
| Artery of Percheron | |
|---|---|
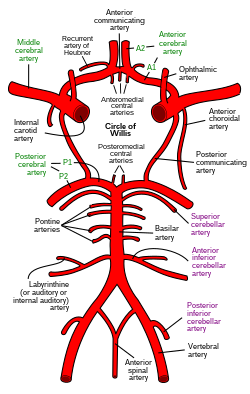
The arterial circle and arteries of the brain. The artery of Percheron (not shown) arise from either the left or right posterior cerebral artery (bottom forks)
|
|
| Details | |
| Source | Posterior cerebral artery |
| Supplies | Both sides of thalamus and midbrain |
|
Anatomical terminology []
|
|
The artery of Percheron (AOP) is a rare anatomic variation in the brain vascularization in which a single arterial trunk arises from the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) to supply both sides of brain structures; the thalamus and midbrain.
The functions of the thalamus and midbrain include the regulation of consciousness, sleep and alertness. Occlusion of the artery of Percheron, for example by a clot, could result in a posterior circulation infarct impairing structures on both sides of the brain. This can produce a bizarre disturbance such as sleep from which the patient cannot be awakened.
The artery of Percheron was first described in 1973 by the French medical scientist Gerard Percheron.
...
Wikipedia
