Anterior scalene
| Scalene muscles | |
|---|---|
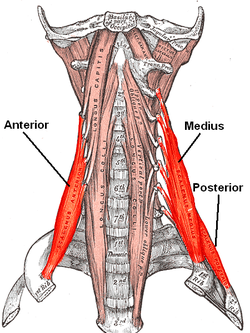
The anterior vertebral muscles.
|
|
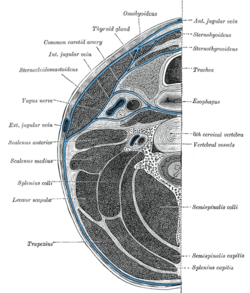
Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli.
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | Cervical vertebrae (CII-CVII) |
| Insertion | First and second ribs |
| Artery |
Ascending cervical artery (branch of Inferior thyroid artery) |
| Nerve | Cervical nerves (C3-C6) |
| Actions | Elevation of first and second ribs |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The scalene muscles (from Greek σκαληνός, or skalenos, meaning uneven as the pairs are all of differing length) are a group of three pairs of muscles in the lateral neck, namely the anterior scalene, middle scalene, and posterior scalene. They are innervated by the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical spinal nerves (C4-C6).
A fourth muscle, the scalenus minimus (Sibson's muscle), is sometimes present behind the lower portion of the anterior scalene.
The scalene muscles originate from the transverse processes from the cervical vertebrae of C2 to C7 and insert onto the first and second ribs, and used to be known as the lateral vertebral muscles.
The anterior scalene muscle (or the scalenus anterior), lies deeply at the side of the neck, behind the sternocleidomastoid muscle. It arises from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae, and descending, almost vertically, is inserted by a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the second rib in front of the subclavian groove. It is supplied by the anterior ramus of cervical nerve 5 and 6.
The middle scalene, (or scalenus medius), is the largest and longest of the three scalene muscles. The middle scalene arises from the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the lower six cervical vertebrae. It descends along the side of the vertebral column to insert by a broad attachment into the upper surface of the first rib, between the tubercle and the subclavian groove. The brachial plexus and the subclavian artery pass anterior to it.
...
Wikipedia
