Sternocleidomastoid muscle
| Sternocleidomastoid | |
|---|---|
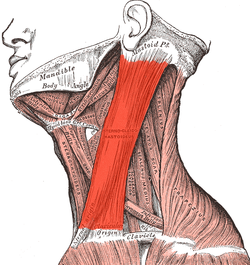
Neck muscles, with the sternocleidomastoid shaded.
|
|

The right sternocleidomastoid can be clearly observed when rotating the head.
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | Manubrium and medial portion of the clavicle |
| Insertion | Mastoid process of the temporal bone, superior nuchal line |
| Artery | Occipital artery and the superior thyroid artery |
| Nerve | Motor: accessory nerve sensory: cervical plexus |
| Actions |
Unilaterally: contralateral cervical rotation, ipsilateral cervical flexion Bilaterally: cervical flexion, elevation of sternum and assists in forced inhalation. |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus sternocleidomastoideus |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
m_22/12550942 |
| TA | A04.2.01.008 |
| FMA | 13407 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
Unilaterally: contralateral cervical rotation, ipsilateral cervical flexion
In human anatomy, the sternocleidomastoid muscle (/ˌstɜːrnoʊˌklaɪdəˈmæsˌtɔɪd, -nə-, -doʊ-/), also known as sternomastoid and commonly abbreviated as SCM, is a paired muscle in the superficial layers of the side of the neck. It is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve.
It is given the name sternocleidomastoid because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (sterno-) and the clavicle (cleido-), and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull.
...
Wikipedia
