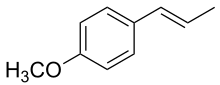
Anethol
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methoxy-4-[(1E)-prop-1-en-1-yl]benzene
|
|
| Other names
(E)-1-Methoxy-4-(prop-1-en-1-yl)benzene
(E)-1-Methoxy-4-(1-propenyl)benzene para-Methoxyphenylpropene p-Propenylanisole Isoestragole trans-1-Methoxy-4-(prop-1-enyl)benzene |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.914 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H12O | |
| Molar mass | 148.21 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.998 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 20 to 21 °C (68 to 70 °F; 293 to 294 K) |
| Boiling point | 234 °C (453 °F; 507 K) (81 °C at 2 mmHg) |
| -96.0·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
|
Related compounds
|
Anisole; Estragole |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Anethole (anise camphor) is an organic compound that is widely used as a flavoring substance. It is a derivative of phenylpropene, a type of aromatic compound that occurs widely in nature, in essential oils. It contributes a large component of the odor and flavor of anise and fennel (both in the botanical family Apiaceae), anise myrtle (Myrtaceae), liquorice (Fabaceae), camphor, magnolia blossoms, and star anise (Illiciaceae). Closely related to anethole is its isomer estragole, abundant in tarragon (Asteraceae) and basil (Lamiaceae), that has a flavor reminiscent of anise. It is a colorless, fragrant, mildly volatile liquid. Anethole is only slightly soluble in water but exhibits high solubility in ethanol. This trait causes certain anise-flavored liqueurs to become opaque when diluted with water, the ouzo effect.
Anethole is an aromatic, unsaturated ether related to lignols. It exists as both cis-trans isomers (see also E-Z notation), involving the double bond outside the ring. The more abundant isomer, and the one preferred for use, is the trans or E isomer.
...
Wikipedia
