AmpC cephalosporinase
| Beta-lactamase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Structure of a Streptomyces albus beta-lactamase
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | β-lactamase domain | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00144 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0013 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001466 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PS00146 | ||||||||
| SCOP | 56601 | ||||||||
| SUPERFAMILY | 56601 | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Available protein structures: | |
|---|---|
| Pfam | structures |
| PDB | RCSB PDB; PDBe; PDBj |
| PDBsum | structure summary |
| β-lactamase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
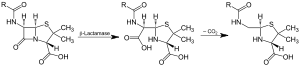
Action of β-lactamase and decarboxylation of the intermediate
|
|||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.5.2.6 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9073-60-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Search | |
|---|---|
| PMC | articles |
| PubMed | articles |
| NCBI | proteins |
Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases, also known as penicillinase) are enzymes (EC 3.5.2.6) produced by bacteria, that provide multi-resistance to β-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a β-lactam. Through hydrolysis, the lactamase enzyme breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.
Beta-lactam antibiotics are typically used to treat a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms are usually secreted, especially when antibiotics are present in the environment.
The structure of a Streptomyces β-lactamase is given by 1BSG.
Penicillinase is a specific type of β-lactamase, showing specificity for penicillins, again by hydrolysing the β-lactam ring. Molecular weights of the various penicillinases tend to cluster near 50 kiloDaltons.
...
Wikipedia
