Amnionitis
| Chorioamnionitis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
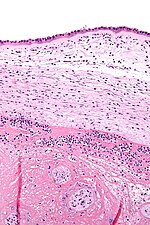
| Micrograph showing chorioamnionitis. The clusters of blue dots are inflammatory cells (neutrophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes). H&E stain. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Obstetrics gynecology |
| ICD-10 | O41.1, P02.7 |
| ICD-9-CM | 658.4, 762.7 |
| DiseasesDB | 31882 |
| eMedicine | ped/89 |
| MeSH | D002821 |
Chorioamnionitis also known as intra-amniotic infection (IAI) is an inflammation of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion) due to a bacterial infection. It typically results from bacteria ascending into the uterus from the vagina and is most often associated with prolonged labor. The risk of developing chorioamnionitis increases with each vaginal examination that is performed in the final month of pregnancy, including during labor.[3]
The amniotic sac consists of two parts:
Chorioamnionitis is diagnosed clinically in the setting of Maternal fever (≥ 100.4 °F) and at least two of the following:
Exclusions:
Chorioamnionitis can be diagnosed from a histologic examination of the fetal membranes.
Infiltration of the chorionic plate by neutrophils is diagnostic of (mild) chorioamnionitis. More severe chorioamnionitis involves subamniotic tissue and may have fetal membrane necrosis and/or abscess formation.
Severe chorioamnionitis may be accompanied by vasculitis of the umbilical blood vessels (due to the fetus' inflammatory cells) and, if very severe, funisitis (inflammation of the umbilical cord's connective tissue).
Antibiotic Treatment consists of:
Completion of treatment/cure is only considered after delivery.
Chorioamnionitis is a risk factor for periventricular leukomalacia and cerebral palsy.
...
Wikipedia
