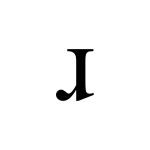
Alveolar approximant
| Alveolar approximant | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ɹ | |||
| ð̠˕ | |||
| IPA number | 151 | ||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ɹ |
||
| Unicode (hex) | U+0279 | ||
| X-SAMPA | r\ or D_r_o |
||
| Kirshenbaum | r |
||
| Braille | |||
|
|||
| Sound | |||
|
|
|||
| Postalveolar approximant | |
|---|---|
| ɹ̠ | |
| Sound | |
|
|
The alveolar approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the alveolar and postalveolar approximants is ⟨ɹ⟩, a lowercase letter r rotated 180 degrees. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ⟨r\⟩.
There is no separate symbol for the dental approximant (as in Spanish nada) in the International Phonetic Alphabet, which most scholars transcribe with the symbol for a voiced dental fricative, ⟨ð⟩.
The most common sound represented by the letter r in English is the postalveolar approximant, pronounced a little more back and transcribed more precisely in IPA as ⟨ɹ̠⟩, but ⟨ɹ⟩ is often used for convenience in its place. For further ease of typesetting, English phonemic transcriptions might use the symbol ⟨r⟩ even though the former symbol represents the alveolar trill in phonetic transcription.
Features of the alveolar approximant:
As an allophone of other rhotic sounds, [ɹ] occurs in Edo, Fula, Murinh-patha, and Palauan.
...
Wikipedia