Alpha-Methylserotonin
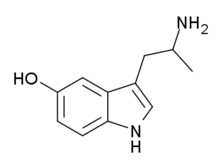
α-Methyl-5-HT
|
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H14N2O |
| Molar mass | 190.242 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
α-Methylserotonin (αMS), also known as α-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (α-methyl-5-HT) or 5-hydroxy-α-methyltryptamine (5-HO-αMT), is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-HT). It acts as a non-selective serotonin receptor agonist and has been used extensively in scientific research to study the function of the serotonin system.
Unlike serotonin, αMS is not metabolized by monoamine oxidase on account of the α-methyl substituent blocking the enzyme's access to the amine. As a result, it has a much longer half-life in comparison. Similarly to serotonin however, αMS poorly crosses the blood-brain-barrier due to its free hydroxyl group, and thus has only weak or no central effects when administered peripherally.
α-Methyltryptophan (αMTP) is a prodrug to αMS which does cross the blood-brain-barrier and thus efficiently delivers αMS into the central nervous system. As a result, αMTP acts as an orally bioavailable false or substitute neurotransmitter for serotonin, and has been suggested as a possible therapeutic agent in the treatment of disorders where serotonin is deficient. The O-methylated analogue of αMS, 5-MeO-αMT, also readily enters the brain and could be used for this purpose as well.
...
Wikipedia
