Acute pharyngitis
| Pharyngitis | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Acute sore throat |
 |
|
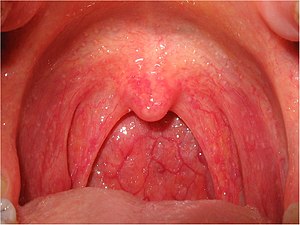
| Viral pharyngitis. Note the redness. | |
| Pronunciation | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Sore throat, fever, runny nose, cough, headache, hoarse voice |
| Complications | Sinusitis, acute otitis media |
| Duration | 3–5 days |
| Causes | Usually viral infection |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, rapid antigen detection test, throat swab |
| Similar conditions | Epiglottitis, thyroiditis, retropharyngeal abscess |
| Treatment | NSAIDs, lidocaine |
| Frequency | ~7.5% of people in any 3-month period |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last three to five days. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is typically a type of respiratory tract infection.
Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults. Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as gonorrhea, fungus, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection such as a cold. Otherwise a rapid antigen detection test (RAPD) or throat swab is recommended. Other conditions that can produce similar symptoms include epiglottitis, thyroiditis, retropharyngeal abscess, and occasionally heart disease.
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen, can be used to help with the pain. Topical lidocaine may also help. Strep throat is typically treated with antibiotics, such as either penicillin or amoxicillin. It is unclear if steroids are useful in acute pharyngitis, other than possibly in severe cases.
...
Wikipedia
