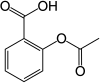
Acetylsalicylic acid
 |
|
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | acetylsalicylic acid /əˌsiːtəlˌsælᵻˈsɪlᵻk/ |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682878 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
by mouth, rectal, lysine acetylsalicylate may be given intravenously or intramuscularly |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80–100% |
| Protein binding | 80–90% |
| Metabolism | Liver, (CYP2C19 and possibly CYP3A), some is also hydrolysed to salicylate in the gut wall. |
| Biological half-life | Dose-dependent; 2 h to 3 h for low doses, 15 h to 30 h for large doses. |
| Excretion | Urine (80–100%), sweat, saliva, feces |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| Synonyms | 2-acetoxybenzoic acid acetylsalicylate acetylsalicylic acid O-acetylsalicylic acid |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.059 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H8O4 |
| Molar mass | 180.157 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
| Density | 1.40 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 135 °C (275 °F) |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (284 °F) (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | 3 mg/mL (20 °C) |
|
|
|
|
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a medication used to treat pain, fever, and inflammation. Specific inflammatory conditions in which it is used include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever. Aspirin given shortly after a heart attack decreases the risk of death. Aspirin is also used long-term to help prevent heart attacks, strokes, and blood clots, in people at high risk. Aspirin may also decrease the risk of certain types of cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. For pain or fever, effects typically begin within 30 minutes. Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and works similar to other NSAIDs but it is also an antiplatelet and suppresses the normal functioning of platelets.
Common side effects include an upset stomach. More significant side effects include stomach ulcers, stomach bleeding, and worsening asthma. Bleeding risk is greater among those who are older, drink alcohol, take other NSAIDs, or are on blood thinners. Aspirin is not recommended in the last part of pregnancy. It is not generally recommended in children with infections because of the risk of Reye's syndrome. High doses may result in ringing in the ears.
...
Wikipedia
