Acesulfame potassium
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
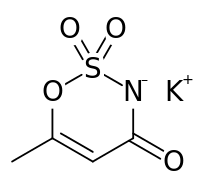
IUPAC name
Potassium 6-methyl-2,2-dioxo-2H-1,2λ6,3-oxathiazin-4-olate
|
|
| Other names
Acesulfame K; Ace K
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
55589-62-3 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL1351474 |
| ChemSpider |
55940 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.269 |
| EC Number | 259-715-3 |
| E number | E950 (glazing agents, ...) |
| PubChem | 23683747 |
| UNII |
23OV73Q5G9 |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H4KNO4S | |
| Molar mass | 201.242 |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.81 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) |
| 270 g/L at 20 °C | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Acesulfame potassium (ace-SUHL-faym), also known as acesulfame K (K is the symbol for potassium) or Ace K, is a calorie-free sugar substitute (artificial sweetener), and marketed under the trade names Sunett and Sweet One. In the European Union, it is known under the E number (additive code) E950. It was discovered accidentally in 1967 by German chemist Karl Clauss at Hoechst AG (now Nutrinova). In chemical structure, acesulfame potassium is the potassium salt of 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide. It is a white crystalline powder with molecular formula C4H4KNO4S and a molecular weight of 201.24 g/mol.
Acesulfame K is 200 times sweeter than sucrose (common sugar), as sweet as aspartame, about 2/3 as sweet as saccharin, and 1/3 as sweet as sucralose. Like saccharin, it has a slightly bitter aftertaste, especially at high concentrations. Kraft Foods patented the use of sodium ferulate to mask acesulfame's aftertaste. Acesulfame K is often blended with other sweeteners (usually sucralose or aspartame). These blends are reputed to give a more sucrose-like taste whereby each sweetener masks the other's aftertaste, or exhibits a synergistic effect by which the blend is sweeter than its components. Acesulfame potassium has a smaller particle size than sucrose, allowing for its mixtures with other sweeteners to be more uniform.
Unlike aspartame, acesulfame K is stable under heat, even under moderately acidic or basic conditions, allowing it to be used as a food additive in baking, or in products that require a long shelf life. Although acesulfame potassium has a stable shelf life, it can eventually degrade to acetoacetamide, which is toxic in high doses. In carbonated drinks, it is almost always used in conjunction with another sweetener, such as aspartame or sucralose. It is also used as a sweetener in protein shakes and pharmaceutical products, especially chewable and liquid medications, where it can make the active ingredients more palatable. The acceptable daily intake of acesulfame potassium is listed as 15 mg/kg/day.
...
Wikipedia

