Acesulfame K
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
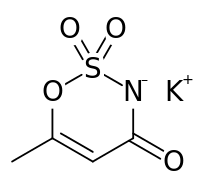
Potassium 6-methyl-2,2-dioxo-2H-1,2λ6,3-oxathiazin-4-olate
|
|
| Other names
Acesulfame K; Ace K
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.269 |
| EC Number | 259-715-3 |
| E number | E950 (glazing agents, ...) |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C4H4KNO4S | |
| Molar mass | 201.242 |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.81 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 225 °C (437 °F; 498 K) |
| 270 g/L at 20 °C | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Acesulfame potassium (/ˌeɪsiːˈsʌlfeɪm/ AY-see-SUL-faym), also known as acesulfame K (K is the symbol for potassium) or Ace K, is a calorie-free sugar substitute (artificial sweetener) often marketed under the trade names Sunett and Sweet One. In the European Union, it is known under the E number (additive code) E950. It was discovered accidentally in 1967 by German chemist Karl Clauss at Hoechst AG (now Nutrinova). In chemical structure, acesulfame potassium is the potassium salt of 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazine-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide. It is a white crystalline powder with molecular formula C
4H
4KNO
4S and a molecular weight of 201.24 g/mol.
Acesulfame K is 200 times sweeter than sucrose (common sugar), as sweet as aspartame, about two-thirds as sweet as saccharin, and one-third as sweet as sucralose. Like saccharin, it has a slightly bitter aftertaste, especially at high concentrations. Kraft Foods patented the use of sodium ferulate to mask acesulfame's aftertaste. Acesulfame K is often blended with other sweeteners (usually sucralose or aspartame). These blends are reputed to give a more sucrose-like taste whereby each sweetener masks the other's aftertaste, or exhibits a synergistic effect by which the blend is sweeter than its components. Acesulfame potassium has a smaller particle size than sucrose, allowing for its mixtures with other sweeteners to be more uniform.
...
Wikipedia

