Acer saccharum
| Sugar maple | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Sugar maple in Brown County State Park, Indiana, USA | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| (unranked): | Angiosperms |
| (unranked): | Eudicots |
| (unranked): | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Species: | A. saccharum |
| Binomial name | |
|
Acer saccharum Marshall |
|
 |
|
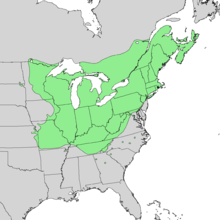
| Natural range of Acer saccharum | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Acer saccharum (sugar maple or rock maple) is a species of maple native to the hardwood forests of eastern Canada, from Nova Scotia west through Quebec and southern Ontario to southeastern Manitoba around Lake of the Woods, and the northern parts of the Central and eastern United States, from Minnesota eastward to the highlands of the eastern states. Sugar maple is best known for its bright fall foliage and for being the primary source of maple syrup.
Acer saccharum is a deciduous tree normally reaching heights of 25–35 m (80–115 ft), and exceptionally up to 45 m (148 ft). A 10-year-old tree is typically about 5 m (16 ft) tall. When healthy, the sugar maple can live for over 400 years.
The leaves are deciduous, up to 20 cm (7.9 in) long and equally wide, with five palmate lobes. The basal lobes are relatively small, while the upper lobes are larger and deeply notched. In contrast with the angular notching of the silver maple, however, the notches tend to be rounded at their interior. The fall color is often spectacular, ranging from bright yellow through orange to fluorescent red-orange, although they look best in the northern part of its range. Sugar maples also have a tendency to color unevenly in fall. In some trees, all colors above can be seen at the same time. They also share a tendency with red maples for certain parts of a mature tree to change color weeks ahead of or behind the remainder of the tree. The leaf buds are pointy and brown-colored. The recent year's growth twigs are green, and turn dark brown.
The flowers are in panicles of five to 10 together, yellow-green and without petals; flowering occurs in early spring after 30–55 growing degree days. The sugar maple will generally begin flowering when it is between 10 and 15 years old. The fruit is a pair of samaras (winged seeds). The seeds are globose, 7–10 mm (9⁄32–13⁄32 in) in diameter, the wing 2–3 cm (3⁄4–1 1⁄4 in) long. The seeds fall from the tree in autumn, where they must be exposed to 90 days of temperatures below −18 °C (0 °F) to break their coating down. Germination of A. saccharum is slow, not taking place until the following spring when the soil has warmed and all frost danger is past. It is closely related to the black maple, which is sometimes included in this species, but sometimes separated as Acer nigrum. The western American bigtooth maple (Acer grandidentatum) is also treated as a variety or subspecies of sugar maple by some botanists.
...
Wikipedia

