1896 Atlantic hurricane season
| 1896 Atlantic hurricane season |

Season summary map
|
| Seasonal boundaries |
| First system formed |
July 4, 1895 |
| Last system dissipated |
November 29, 1895 |
| Strongest storm |
|
| Name |
Two |
| • Maximum winds |
115 mph (185 km/h) |
| • Lowest pressure |
956 mbar (hPa; 28.23 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics |
| Total storms |
7 |
| Hurricanes |
6 |
Major hurricanes
(Cat. 3+) |
2 |
| Total fatalities |
286 |
| Total damage |
> $10 million (1896 USD) |
|
|
Atlantic hurricane seasons
1894, 1895, 1896, 1897, 1898
|
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
July 4 – July 9 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
August 30 – September 10 |
| Peak intensity |
115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min) 956 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 18 – September 28 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
September 22 – September 30 |
| Peak intensity |
125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min) 960 mbar (hPa) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 7 – October 13 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
October 26 – November 9 |
| Peak intensity |
100 mph (155 km/h) (1-min) |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) |
|
|
| Duration |
November 27 – November 29 |
| Peak intensity |
60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min) |
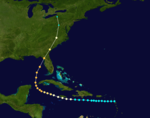
The 1896 Atlantic hurricane season was fairly inactive but produced one of the costliest hurricanes ever to strike the United States until that point, along with several other destructive tropical cyclones. The season began in early July with a hurricane in the Gulf of Mexico and ended in late November with a slow-moving tropical storm over the Lesser Antilles. Of the season's seven documented systems, six are believed to have become hurricanes, and two intensified into major hurricanes—the equivalence of Category 3 or greater on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson scale. All but one of the systems directly affected land to some degree; Hurricane "Six" remained over open water and only posed a threat to shipping lanes. In addition, a possible storm was identified off the coast of North Carolina on August 28–29, but modern reanalysis efforts have found insufficient evidence to classify it as a tropical cyclone. Tropical systems in the 1896 season killed at least 286 people and inflicted more than $10 million (1896 USD) in damage.
The first hurricane made landfall in the Florida Panhandle on July 7, causing wind damage and coastal flooding in Pensacola, and destroying boats at port. No activity was observed until late August when a hurricane triggered widespread river flooding in Puerto Rico. After moving north, this storm struck eastern New England. Hurricane "Three" avoided land, but its outer periphery generated gusty winds in the Outer Banks of North Carolina. On September 29, fast-moving Hurricane "Four" became one of the costliest United States hurricanes on record at the time after swamping Florida's Cedar Keys with a large storm surge and subsequently causing extensive devastation in the eastern United States. The hurricane caused 202 deaths and more than $9 million in damage across eight states, plus Washington, D.C. and the Great Lakes. About two weeks later, Hurricane "Five" roughly paralleled the U.S. East Coast, causing substantial coastal flooding and destruction of beachfront property. Little is known about the season's sixth hurricane which never affected land. Torrential rainfall associated with the final tropical storm of the season triggered deadly flooding on Montserrat, where nearly 50 people drowned and many more lost their homes.
...
Wikipedia