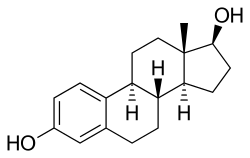
17β-estradiol
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌɛstrəˈdaɪoʊl/ ES-trə-DYE-ohl |
|
IUPAC name
(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13-Methyl-6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-decahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol
|
|
| Other names
Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol; 17β-Estradiol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.022 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C18H24O2 | |
| Molar mass | 272.38 g/mol |
| -186.6·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Pharmacology | |
| G03CA03 (WHO) | |
| Oral, sublingual, intranasal, topical/transdermal, vaginal, intramuscular or subcutaneous (as an ester), subdermal implant | |
| Pharmacokinetics: | |
| Oral: <5% | |
| ~98%: • Albumin: 60% • SHBG: 38% • Free: 2% |
|
| Liver (via hydroxylation, sulfation, glucuronidation) | |
| Oral: 13–20 hours Sublingual: 8–18 hours Topical (gel): 36.5 hours |
|
|
Urine: 54% Feces: 6% |
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Estradiol (E2), also spelled oestradiol, is a steroid, an estrogen, and the primary female sex hormone. It is named for and is important in the regulation of the estrous and menstrual female reproductive cycles. Estradiol is essential for the development and maintenance of female reproductive tissues such as the breasts, uterus, and vagina during puberty, adulthood, and pregnancy, but it also has important effects in many other tissues, including bone, fat, skin, liver, and the brain. While estrogen levels in men are lower compared to those in women, estrogens have essential functions in men, as well. It is found in most vertebrates and crustaceans, insects, fish, and other animal species.
Estradiol is produced especially within the follicles of the female ovaries, but also in other endocrine (i.e., hormone-producing) and nonendocrine tissues (e.g., including fat, liver, adrenal, breast, and neural tissues). Estradiol is biosynthesized from cholesterol through a series of chemical intermediates. One principal pathway involves the generation of androstenedione, which is converted into estrone by aromatase and then by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase into estradiol. Alternatively, androstenedione can be converted into testosterone, an androgen and the primary male sex hormone, which in turn can be aromatized into estradiol.
...
Wikipedia
