Zinc pyrithione
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
bis(2-pyridylthio)zinc 1,1'-dioxide
|
|
| Other names
ZnP, pyrithione zinc, zinc OMADINE
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.324 |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C10H8N2O2S2Zn | |
| Molar mass | 317.70 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless solid |
| Melting point | 240 °C (464 °F; 513 K) (decomposition) |
| Boiling point | decomposes |
| 8 ppm (pH 7) | |
| Pharmacology | |
| D11AX12 (WHO) | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Zinc pyrithione (or pyrithione zinc) is a coordination complex of zinc. It has fungistatic (that is, it inhibits the division of fungal cells) and bacteriostatic (inhibits bacterial cell division) properties and is used in the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis.
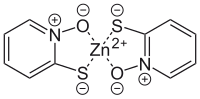
The pyrithione ligands, which are formally monoanions, are chelated to Zn2+ via oxygen and sulfur centers. In the crystalline state, zinc pyrithione exists as a centrosymmetric dimer (see figure), where each zinc is bonded to two sulfur and three oxygen centers. In solution, however, the dimers dissociate via scission of one Zn-O bond.
This compound was first described in the 1930s.
Pyrithione is the conjugate base derived from 2-mercaptopyridine-N-oxide (CAS# 1121-31-9), a derivative of pyridine-N-oxide.
Zinc pyrithione is best known for its use in treating dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis, particularly in dandruff shampoos. It also has antibacterial properties and is effective against many pathogens from the and Staphylococcus genera. Its other medical applications include treatments of psoriasis, eczema, ringworm, fungus, athletes foot, dry skin, atopic dermatitis, tinea, and vitiligo.
...
Wikipedia
