Yokuts languages
| Yokutsan | |
|---|---|
| Mariposan | |
| Ethnicity | Yokut |
| Geographic distribution |
San Joaquin Valley, California |
| Linguistic classification |
Yok-Utian
|
| Subdivisions | |
| ISO 639-3 | [http://www.ethnologue.com/language/yok yok yok] |
| Glottolog | yoku1255 |
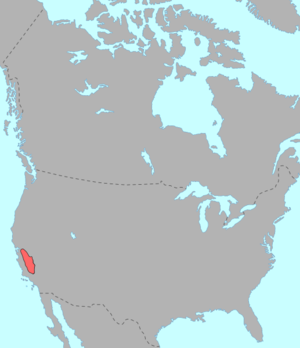
Pre-contact distribution of Yokutsan languages
|
|
Yokutsan (also known as Yokuts and Mariposan) is an endangered language family spoken in the interior of Northern and Central California in and around the San Joaquin Valley by the Yokut people. The speakers of Yokutsan languages were severely affected by disease, missionaries, and the Gold Rush. While descendants of Yokutsan-family speakers currently number in the thousands, most of the constituent languages are now extinct.
The Yawelmani dialect of Valley Yokuts has been a focus of much linguistic research.
The Yokutsan family consists of half a dozen languages, depending upon one's definition of the boundary between a language and a dialect. An estimated forty linguistically distinct groups existed before Euro-American contact. The following classification appears in Whistler & Golla (1986).
Poso Creek
General Yokuts (all others)
Many Yokutsan varieties are extinct, as noted above. Those that are still spoken are endangered.
In recent years, Choinimni, Wikchamni, Chukchansi, Kechayi, Tachi, and Yawelmani all had a few fluent speakers and a variable number of partial speakers. Wikchamni, Chukchansi, Tachi, and Yawelmani were being taught to at least a few children during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
Chukchansi is now a written language, with its own alphabet developed on a federal grant. Chukchansi also has a phrase book and dictionary that are partially completed. In May 2012, the Linguistics Department of Fresno State University received a $1 million grant to compile a Chuckchansi dictionary and grammar texts, and to "provide support for scholarships, programs, and efforts to assemble native texts and create a curriculum for teaching the language so it can be brought back into social and ritual use."
...
Wikipedia
