Windows 9x
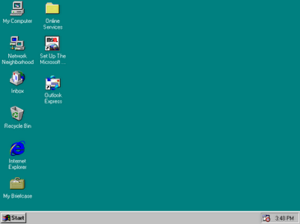
Screenshot of Windows 95, the first version of Windows in the 9x series
|
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Working state | Discontinued |
| Source model | Closed source |
| Platforms | IA-32 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic |
| Userland | Windows API |
| Default user interface | Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
Windows 9x is a generic term referring to a series of Microsoft Windows computer operating systems produced from 1995 to 2000, which were based on the Windows 95 kernel and its underlying foundation of MS-DOS, both of which were updated in subsequent versions. This includes all versions of Windows 95 and Windows 98. Windows ME is sometimes included.
Windows 9x is predominantly known for its use in desktops. In 1998, Windows made up 82% of operating system market share.
Internal release versions for versions of Windows 9x are 4.x. Previous MS-DOS based versions of Windows used version numbers of 3.2 or lower. Windows NT, which was aimed at professional users such as networks and businesses, used a similar but separate version number between 3.1 and 4.0.
The final version of Windows 9x was Windows ME, released in September 2000 with an internal version number of 4.9. All future versions of Windows, starting with Windows 2000 and Windows XP, would be based on the Windows NT codebase.
The first independent version of Microsoft Windows, version 1.0, released on 20 November 1985, achieved little popularity. It was originally going to be called "Interface Manager" but Rowland Hanson, the head of marketing at Microsoft, convinced the company that the name Windows would be more appealing to consumers. Windows 1.0 was not a complete operating system, but rather an "operating environment" that extended MS-DOS, and shared the latter's inherent flaws and problems.
The second release of Microsoft Windows, version 2.0, came out on 9 December 1987, and used the real-mode memory model, which confined it to a maximum of 1 megabyte of memory. In such a configuration, it could run under another multitasking system like DESQview, which used the 286 Protected Mode.
...
Wikipedia
