Whiplash (medicine)
| Whiplash | |
|---|---|
 |
|
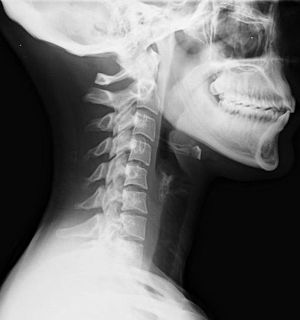
| Lateral view X-ray of whiplash showing a loss of normal lordosis of the cervical spine | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Orthopedics |
| ICD-10 | S13.4 |
| ICD-9-CM | 847.0 |
| DiseasesDB | 14122 |
| MedlinePlus | 000025 |
| MeSH | D014911 |
Whiplash is a non-medical term describing a range of injuries to the neck caused by or related to a sudden distortion of the neck associated with extension, although the exact injury mechanisms remain unknown. The term "whiplash" is a colloquialism. "Cervical acceleration–deceleration" (CAD) describes the mechanism of the injury, while the term "whiplash associated disorders" (WAD) describes the injury sequelae and symptoms.
Whiplash is commonly associated with motor vehicle accidents, usually when the vehicle has been hit in the rear; however, the injury can be sustained in many other ways, including headbanging, bungee jumping and falls. It is one of the main injuries covered by insurance. In the United Kingdom, 430,000 people made an insurance claim for whiplash in 2007, accounting for 14% of every driver's premium.
Before the invention of the car, whiplash injuries were called "railway spine" as they were noted mostly in connection with train collisions. The first case of severe neck pain arising from a train collision was documented around 1919. The number of whiplash injuries has since risen sharply due to rear-end motor vehicle collisions. Given the wide variety of symptoms associated with whiplash injuries, the Quebec Task Force on Whiplash-Associated Disorders coined the phrase 'Whiplash-Associated Disorders'.
Symptoms reported by sufferers include: pain and aching to the neck and back, referred pain to the shoulders, sensory disturbance (such as pins and needles) to the arms and legs, and headaches. Symptoms can appear directly after the injury, but often are not felt until days afterwards. Whiplash is usually confined to the spine. The most common areas of the spine affected by whiplash are the neck and middle of the spine. "Neck" pain is very common between the shoulder and the neck. The "missing link" of whiplash may be towards or inside the shoulder and this would explain why neck therapy alone frequently does not give lasting relief.
Cognitive symptoms following whiplash trauma, such as being easily distracted or irritated, seems to be common and possibly linked to a poorer prognosis.
...
Wikipedia
