West Gulf Blockading Squadron
| Union Blockade | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the American Civil War | |||||||
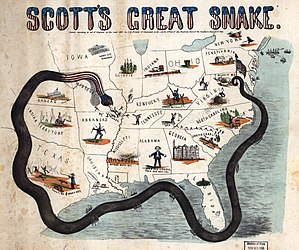 A 1861 characterized map of the Union blockade, known as Winfield Scott's Anaconda Plan |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
|
||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
|
||||||
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederacy from trading.
The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of 3,500 miles of Atlantic and Gulf coastline, including 12 major ports, notably New Orleans and Mobile. Those blockade runners fast enough to evade the Union Navy could only carry a small fraction of the supplies needed. They were operated largely by British citizens, making use of neutral ports such as Havana, Nassau and Bermuda. The Union commissioned around 500 ships, which destroyed or captured about 1,500 blockade runners over the course of the war.
On April 19, 1861, President Lincoln issued a Proclamation of Blockade Against Southern Ports:
Whereas an insurrection against the Government of the United States has broken out in the States of South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Florida, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas, and the laws of the United States for the collection of the revenue cannot be effectually executed therein comformably to that provision of the Constitution which requires duties to be uniform throughout the United States:
And whereas a combination of persons engaged in such insurrection, have threatened to grant pretended letters of marque to authorize the bearers thereof to commit assaults on the lives, vessels, and property of good citizens of the country lawfully engaged in commerce on the high seas, and in waters of the United States: And whereas an Executive Proclamation has been already issued, requiring the persons engaged in these disorderly proceedings to desist therefrom, calling out a militia force for the purpose of repressing the same, and convening Congress in extraordinary session, to deliberate and determine thereon:
...
Wikipedia
