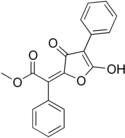
Vulpinic acid
|
|
|||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
IUPAC name
Methyl (2E)-2-(5-hydroxy-3-oxo-4-phenylfuran-2-ylidene)-2-phenylacetate
|
|||
| Identifiers | |||
|
3D model (Jmol)
|
|||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.560 | ||
|
PubChem CID
|
|||
|
|||
| Properties | |||
| C19H14O5 | |||
| Molar mass | 322.32 g·mol−1 | ||
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|||
|
|
|||
| Infobox references | |||
Vulpinic acid is a naturally occurring pulvinic acid derivative found in several lichen species, as well as some non-lichenized fungi. It was first isolated in 1925. It is bright yellow, and relatively toxic.
Vulpinic acid was first isolated from lichens, and is a secondary metabolite of the fungal partner. It is speculated that vulpinic acid's biological function is as a repellent for some herbivores. Humans have also exploited this toxicity by using lichens that contain high amounts of the chemical (such as Letharia vulpina) as poison for wolves and foxes. The substance showed also some antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria and has even been shown to disrupt cell division in MRSA.
...
Wikipedia