Vorinostat
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /vɒˈrɪnoʊstæt/ vorr-IN-oh-stat |
| Trade names | Zolinza |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607050 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 1.8–11% |
| Protein binding | ~71% |
| Metabolism |
Hepatic glucuronidation and β-oxidation system not involved |
| Metabolites | vorinostat O-glucuronide, 4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid (both inactive) |
| Biological half-life | ~2 hours (vorinostat and O-glucuronide), 11 hours (4-anilino-4-oxobutanoic acid) |
| Excretion | Renal (negligible) |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.207.822 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
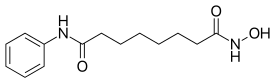
| Formula | C14H20N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 264.32 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vorinostat (rINN) also known as suberanilohydroxamic acid (suberoyl+anilide+hydroxamic acid abbreviated as SAHA) is a member of a larger class of compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases (HDAC). Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDI) have a broad spectrum of epigenetic activities.
Vorinostat is marketed under the name Zolinza (/zoʊˈlɪnzə/ zoh-LIN-zə) by Merck for the treatment of cutaneous manifestations in patients with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) when the disease persists, gets worse, or comes back during or after two systemic therapies. The compound was developed by Columbia University chemist Ronald Breslow and Memorial Sloan-Kettering researcher Paul Marks.
Vorinostat was the first histone deacetylase inhibitor approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of CTCL on October 6, 2006. It also failed to demonstrate efficacy in treating acute myeloid leukemia in a phase II study.
Vorinostat has been shown to bind to the active site of histone deacetylases and act as a chelator for zinc ions also found in the active site of histone deacetylases. Vorinostat's inhibition of histone deacetylases results in the accumulation of acetylated histones and acetylated proteins, including transcription factors crucial for the expression of genes needed to induce cell differentiation.
...
Wikipedia
