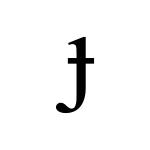
Voiced palatal stop
| Voiced palatal stop | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ɟ | |||
| IPA number | 108 | ||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ɟ |
||
| Unicode (hex) | U+025F | ||
| X-SAMPA | J\ |
||
| Kirshenbaum | J |
||
| Braille |
|
||
|
|||
| Sound | |||
|
|
|||
The voiced palatal stop or voiced palatal plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some vocal languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɟ⟩, a barred dotless ⟨j⟩ that was initially created by turning the type for a lowercase letter ⟨f⟩. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is J\.
If the distinction is necessary, the voiced alveolo-palatal stop may be transcribed ⟨ɟ̟⟩, ⟨ɟ˖⟩ (both symbols denote an advanced ⟨ɟ⟩) or ⟨d̠ʲ⟩ ([relative articulation#Advanced and retracted|retracted]] and palatalized ⟨d⟩), but they are essentially equivalent since the contact includes both the blade and body (but not the tip) of the tongue. The equivalent X-SAMPA symbols are J\_+ and d_-' or d_-_j, respectively. There is also a non-IPA letter ⟨ȡ⟩ ("d" with the curl found in the symbols for alveolo-palatal sibilant fricatives ⟨ɕ, ʑ⟩), used especially in Sinological circles.
The sound does not exist as a phoneme in English, but it is perhaps most similar to a voiced postalveolar affricate [d͡ʒ], as in English jump. Because it is difficult to get the tongue to touch just the hard palate without also touching the back part of the alveolar ridge,[ɟ] is a less common sound worldwide than [d͡ʒ]. It is also common for the symbol ⟨ɟ⟩ to be used to represent a palatalized voiced velar stop or palato-alveolar/alveolo-palatal affricates, as in Indic languages. That may be considered appropriate when the place of articulation needs to be specified, and the distinction between stop and affricate is not contrastive.
...
Wikipedia