Vitreous hemorrhage
| Vitreous hemorrhage | |
|---|---|
 |
|
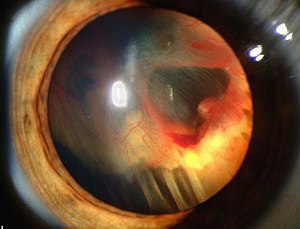
| Slit lamp photograph showing retinal detachment with visible vitreous hemorrhage. | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | ophthalmology |
| ICD-10 | H43.1 |
| ICD-9-CM | 379.23 |
Vitreous hemorrhage is the extravasation, or leakage, of blood into the areas in and around the vitreous humor of the eye. The vitreous humor is the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eye. A variety of conditions can result in blood leaking into the vitreous humor, which can cause impaired vision, floaters, and photopsia.
There are many factors known to cause vitreous hemorrhage.
The most common cause found in adults is diabetic retinopathy. Abnormal blood vessels can form in the back of the eye of a person with diabetes. These new blood vessels are weaker and prone to breaking and causing hemorrhage. Diabetic retinopathy accounts for 31.5-54% of all cases of vitreous hemorrhage in adults in the United States.
Some injuries can cause blood vessels in the back of the eye to bleed. Trauma is the leading cause of vitreous hemorrhage in young people, and accounts for 12–18.8% of cases in adults.
A tear in the retina can allow fluids from the eye to leak in behind the retina, which causes retinal detachment. When this occurs, blood from the retinal blood vessels can bleed into the vitreous.Retinal tear accounts for 11.4–44% of vitreous hemorrhage cases.
As one gets older, pockets of fluid can develop in the vitreous. When these pockets develop near the back of the eye, the vitreous can pull away from the retina and possibly tear it. Posterior vitreous detachment accounts for 3.7–11.7% of vitreous hemorrhage cases.
Less common causes of vitreous hemorrhage make up 6.4–18% of cases, and include:
Common symptoms of vitreous hemorrhage include:
Small vitreous hemorrhage often manifests itself as "floaters". A moderate case will often result in dark streaks in the vision, while dense vitreous hemorrhage can significantly inhibit vision.
Vitreous hemorrhage is diagnosed by identifying symptoms, examining the eye, and performing tests to identify cause. Some common tests include:
The treatment method used depends on the cause of the hemorrhage. In most cases, the patient is advised to rest with the head elevated 30–45°, and sometimes to put patches over the eyes to limit movement prior to treatment in order to allow the blood to settle. The patient is also advised to avoid taking medications that cause blood thinning (such as aspirin or similar medications).
...
Wikipedia
