Viral entry
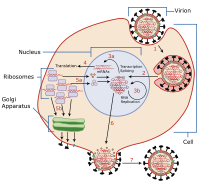
Viral entry is the earliest stage of infection in the viral life cycle, as the virus comes into contact with the host cell and introduces viral material into the cell. The major steps involved in viral entry are shown below. Despite the variation among viruses, there are several shared generalities concerning viral entry.
A virus floating around an enclosed space with possible host cells faces a large hurdle, the thermodynamics of diffusion. Because neutrally charged objects do not naturally clump around each other, the virus must find a way to move even near a host cell. It does this by attachment -- or adsorption --- onto a susceptible cell; a cell which holds a receptor that the virus can bind to. The receptors on the viral envelope effectively become connected to complementary receptors on the cell membrane. This attachment causes the two membranes to remain in mutual proximity, favoring further interactions between surface proteins. This is also the first requisite that must be satisfied before a cell can become infected. Satisfaction of this requisite makes the cell susceptible. Viruses that exhibit this behavior include many enveloped viruses such as HIV and Herpes simplex virus
This basic idea extends to viruses that do not contain an envelope. Well studied examples are the viruses that infect bacteria, known as bacteriophages or simply phages. Typical phages have long tails used to attach to receptors on the bacterial surface.
Prior to entry, a virus must attach to a host cell. Attachment is achieved when receptors on the capsid or viral envelope become connected to complementary receptor proteins on the cell membrane of the target cell. A virus must now enter the cell, which is covered by a phospholipid bilayer, a cell's natural barrier to the outside world. The process by which this barrier is breached depends upon the virus. Types of entry are:
...
Wikipedia