Vidarabine
 |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| ATC code | J05AB03 (WHO) S01AD06 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 24-38% |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
| CAS Number |
24356-66-9 |
| PubChem (CID) | 21704 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 4806 |
| DrugBank |
DB00194 |
| ChemSpider |
20400 |
| UNII |
FA2DM6879K |
| KEGG |
D00406 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1090 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 007328 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.203.402 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
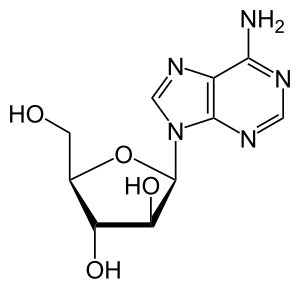
| Formula | C10H15N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 285.257 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vidarabine or 9-β-D-arabinofuranosyladenine (ara-A) is an antiviral drug which is active against herpes simplex and varicella zoster viruses.
In the 1950s two nucleosides were isolated from the Caribbean sponge Tethya crypta: spongothymidine and spongouridine; which contained D-arabinose rather than D-ribose. These compounds led to the synthesis of a new generation, sugar modified nucleoside analog vidarabine, and the related compound cytarabine. In 2004 these were the only marine related compounds in clinical use.
The drug was first synthesized in 1960 in the Bernard Randall Baker lab at the Stanford Research Institute (now SRI International).
The drug was originally intended as an anti-cancer drug. The anti-viral activity of vidarabine was first described by M. Privat de Garilhe and J. De Rudder in 1964. It was the first nucleoside analog antiviral to be given systemically and was the first agent to be licensed for the treatment of systematic herpes virus infection in humans. It was University of Alabama at Birmingham researcher and physician Richard J. Whitley in 1976 where the clinical effectiveness of vidarabine was first realized, and vidarabine was used in the treatment of many viral diseases.
Vidarabine is an analog of adenosine with the D-ribose, replaced with D-arabinose. As you can see from figure 1.1 that it is a stereoisomer of adenosine. It has a half-life of 60 minutes, and its solubility is 0.05%, and is able to cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB) when converted to its active metabolite.
...
Wikipedia

