Vestibulospinal tract
| Vestibulospinal tract | |
|---|---|

Vestibulospinal tract is labeled, in red at bottom left.
|
|
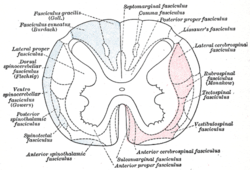
Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord. (Vestibulospinal fasciculus labeled at bottom right.)
|
|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus vestibulospinalis |
| NeuroLex ID | Vestibulospinal tract |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
t_15/12817329 |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
| Medulla Spinalis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Details | |
| Latin | medulla spinalis |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
The vestibulospinal tract is a neural tract in the central nervous system. Specifically, it is a component of the extrapyramidal system and is classified as a component of the medial pathway. Like other descending motor pathways, the vestibulospinal fibers of the tract relay information from nuclei to motor neurons. The vestibular nuclei receive information through the vestibulocochlear nerve about changes in the orientation of the head. The nuclei relay motor commands through the vestibulospinal tract. The function of these motor commands is to alter muscle tone, extend, and change the position of the limbs and head with the goal of supporting posture and maintaining balance of the body and head.
The vestibulospinal tract is part of the "extrapyramidal system" of the central nervous system. In human anatomy, the extrapyramidal system is a neural network located in the brain that is part of the motor system involved in the coordination of movement. The system is called "extrapyramidal" to distinguish it from the tracts of the motor cortex that reach their targets by traveling through the "pyramids" of the medulla. The pyramidal pathways, such as corticospinal and some corticobulbar tracts, may directly innervate motor neurons of the spinal cord or brainstem. This is seen in anterior (ventral) horn cells or certain cranial nerve nuclei. Whereas the extrapyramidal system centers around the modulation and regulation through indirect control of anterior (ventral) horn cells. The extrapyramidal subcortical nuclei include the substantia nigra, caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, thalamus, red nucleus and subthalamic nucleus.
...
Wikipedia
