Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
| Ventromedial prefrontal cortex | |
|---|---|
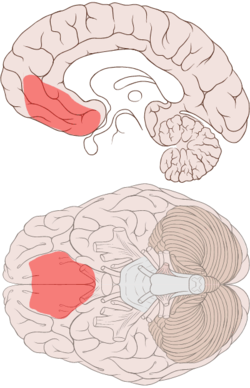
Ventromedial prefrontal cortex shown on medial and ventral views of the brain, reflecting approximate location of damage in patients with decision making deficits.
|
|

Medial surface of the brain with Brodmann's areas numbered.
|
|
| Details | |
| Latin | Cortex praefrontalis ventromedialis |
|
Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
[]
|
|
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) is a part of the prefrontal cortex in the mammalian brain. The ventral medial prefrontal is located in the frontal lobe at the bottom of the cerebral hemispheres and is implicated in the processing of risk and fear. It also plays a role in the inhibition of emotional responses, and in the process of decision making.
While the ventromedial prefrontal cortex does not have a universally agreed on demarcation, in most sources, it is equivalent to the ventromedial reward network of Ongur and Price. This network includes Brodmann area 10, Brodmann area 14, Brodmann area 25, and Brodmann area 32, as well as portions of Brodmann area 11, Brodmann area 12, and Brodmann area 13. However, not all sources agree on the boundaries of the area. Different researchers use the term ventromedial prefrontal cortex differently. Sometimes, the term is saved for the area above the medial orbitofrontal cortex, while at other times, 'ventromedial prefrontal cortex' is used to describe a broad area in the lower (ventral) central (medial) region of the prefrontal cortex, of which the medial orbitofrontal cortex constitutes the lowermost part. This latter, broader area, corresponds to the area damaged in patients with decision-making impairments investigated by António Damásio and colleagues (see diagram, and below).
To get a rough idea of where the ventromedial prefrontal cortex is, recall that the left and right hemispheres of the brain are separated [by the longitudinal cerebral fissure]. Now imagine you could take your hand and starting at the anterior brain (where your forehead is) insert it into this gap until you reached the insula (a structure that is beneath the frontal lobe). Your palm would be touching a part of the prefrontal cortex, which is in the front part of the brain and the lower part of your palm would be touching the ventral medial prefrontal cortex.
...
Wikipedia
