Vena cava inferior
| Inferior vena cava | |
|---|---|
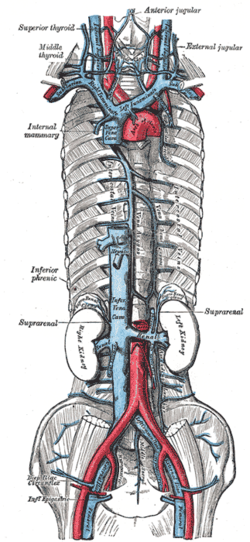
Superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, azygos vein and their tributaries
|
|
| Details | |
| Source |
common iliac vein lumbar veins testicular vein renal vein suprarenal vein hepatic vein |
| Drains to | right atrium |
| Artery | abdominal aorta |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena cava inferior |
| MeSH | A07.231.908.949.648 |
| TA | A12.3.09.001 |
| FMA | 10951 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
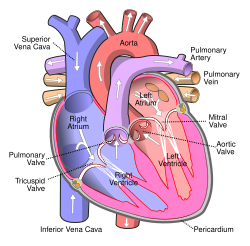
The inferior vena cava (or IVC) (Latin: vena, "vein", cavus, "hollow") is a large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. Its walls are rigid and has valves so the blood does not flow down via gravity. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra.
The inferior vena cava is the lower ("inferior") of the two venae cavae, the two large veins that carry deoxygenated blood from the body: the inferior vena cava carries blood from the lower half of the body whilst the superior vena cava carries blood from the upper half of the body.
It is a large retroperitoneal vein that lies posterior to the abdominal cavity and runs along the right side of the vertebral column. It enters the right atrium at the lower right, back side of the heart.
The inferior vena cava is formed by the joining of the left and right common iliac veins and brings collected blood into the right atrium of the heart. It also joins with the azygos vein (which runs on the right side of the vertebral column) and venous plexuses next to the spinal cord.
...
Wikipedia