Vaginal examination
| Pap test | |
|---|---|
| Intervention | |
 |
|
| ICD-9-CM | 795.00 |
| MeSH | D014626 |
| MedlinePlus | 003911 |
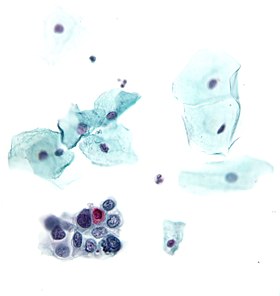
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, known earlier as Pap smear, cervical smear, or smear test) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially pre-cancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures, and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was invented by, and named for, the prominent Greek doctor Georgios Papanikolaou.
A Pap smear is performed by opening the vaginal canal with a speculum, then collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells). The collected cells are examined under a microscope to look for abnormalities. The test aims to detect potentially pre-cancerous changes (called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical dysplasia; the squamous intraepithelial lesion system (SIL) is also used to describe abnormalities), which are caused by human papillomavirus, a sexually transmitted DNA virus. The test remains an effective, widely used method for early detection of pre-cancer and cervical cancer. While the test may also detect infections and abnormalities in the endocervix and endometrium, it is not designed to do so.
In the United States, Pap smear screening is recommended starting around 21 years of age until the age of 65. However, other countries do not recommend pap testing in non-sexually active women. Guidelines on frequency vary from every three to five years. If results are abnormal, and depending on the nature of the abnormality, the test may need to be repeated in six to twelve months. If the abnormality requires closer scrutiny, the patient may be referred for detailed inspection of the cervix by colposcopy. The woman may also be referred for HPV DNA testing, which can serve as an adjunct to Pap testing. Additional biomarkers which may be applied as ancillary tests with the Pap test are evolving.
...
Wikipedia
