Upper respiratory tract infection
| Upper respiratory tract infection | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conducting passages. | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Frequency | 17.2 billion (2015) |
| Deaths | 3,100 |
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
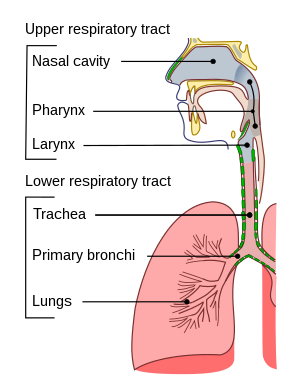
Upper respiratory tract infections (URI or URTI) are illnesses caused by an acute infection which involves the upper respiratory tract including the nose, sinuses, pharynx or larynx. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold. Most infections are viral in nature and in other instances the cause is bacterial. Upper respiratory tract infections can also be fungal or helminth in origin, but these are far less common.
In 2015, 17.2 billion cases of upper respiratory infections occurred. As of 2014, upper respiratory infections caused about 3,000 deaths down from 4,000 in 1990.
A URI may be classified by the area inflammed. Rhinitis affects the nasal mucosa, while rhinosinusitis or sinusitis affects the nose and paranasal sinuses, including frontal, ethmoid, maxillary, and sphenoid sunuses. Nasopharyngitis (rhinopharyngitis or the common cold) affects the nares, pharynx, hypopharynx, uvula, and tonsils generally. Without involving the nose, pharyngitis inflames the pharynx, hypopharynx, uvula, and tonsils. Similarly, epiglottitis (supraglottitis) inflames the superior portion of the larynx and supraglottic area; laryngitis is in the larynx; laryngotracheitis is in the larynx, trachea, and subglottic area; and tracheitis is in the trachea and subglottic area.
...
Wikipedia
