Ubaid culture
 |
|
| Geographical range | Mesopotamia |
|---|---|
| Period | Chalcolithic |
| Dates | c. 6500 — c. 3800 BC |
| Type site | Tell al-`Ubaid |
| Major sites | Eridu |
| Preceded by | Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period, Hassuna culture, Samarra culture |
| Followed by | Uruk period |
farming, animal husbandry
pottery, metallurgy, wheel
circular ditches, henges, megaliths
Neolithic religion
The Ubaid period (c. 6500 to 3800 BC) is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The name derives from Tell al-`Ubaid where the earliest large excavation of Ubaid period material was conducted initially by Henry Hall and later by Leonard Woolley.
In South Mesopotamia the period is the earliest known period on the alluvial plain although it is likely earlier periods exist obscured under the alluvium. In the south it has a very long duration between about 6500 and 3800 BC when it is replaced by the Uruk period.
In North Mesopotamia the period runs only between about 5300 and 4300 BC. It is preceded by the Halaf period and the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period and succeeded by the Late Chalcolithic period.
The term "Ubaid period" was coined at a conference in Baghdad in 1930, where at the same time the Jemdet Nasr and Uruk periods were defined.
The Ubaid period is divided into three principal phases:
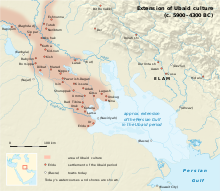
Spreading from Eridu, the Ubaid culture extended from the Middle of the Tigris and Euphrates to the shores of the Persian Gulf, and then spread down past Bahrain to the copper deposits at Oman. The archaeological record shows that Arabian Bifacial/Ubaid period came to an abrupt end in eastern Arabia and the Oman peninsula at 3800 BC, just after the phase of lake lowering and onset of dune reactivation. At this time, increased aridity led to an end in semi-desert nomadism, and there is no evidence of human presence in the area for approximately 1,000 years, the so-called "Dark Millennium". That might be due to the 5.9 kiloyear event at the end of the Older Peron.
...
Wikipedia
