Tyrannosauridae
| Tyrannosaurids Temporal range: Late Cretaceous, 80–66 Ma |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
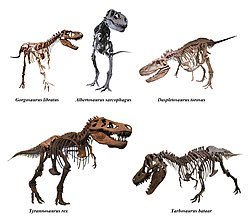
| Skeletal reconstructions of various tyrannosaurids | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | Theropoda |
| Superfamily: | †Tyrannosauroidea |
| Family: |
†Tyrannosauridae Osborn, 1906 |
| Type species | |
|
†Tyrannosaurus rex Osborn, 1905 |
|
| Subgroups | |
|
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Deinodontidae Cope, 1866 |
|
Deinodontidae Cope, 1866
Aublysodontidae Nopcsa, 1928
Shanshanosauridae Dong, 1977
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs which comprises two subfamilies containing up to eleven genera, including the eponymous Tyrannosaurus. The exact number of genera is controversial, with some experts recognizing as few as three. All of these animals lived near the end of the Cretaceous Period and their fossils have been found only in North America and Asia.
Although descended from smaller ancestors, tyrannosaurids were almost always the largest predators in their respective ecosystems, putting them at the apex of the food chain. The largest species was Tyrannosaurus rex, one of the largest known land predators, which measured up to 12.3 metres (40 ft) in length and up to 10.2 tonnes (11.2 short tons) in weight. Tyrannosaurids were bipedal carnivores with massive skulls filled with large teeth. Despite their large size, their legs were long and proportioned for fast movement. In contrast, their arms were very small, bearing only two functional digits.
Unlike most other groups of dinosaurs, very complete remains have been discovered for most known tyrannosaurids. This has allowed a variety of research into their biology. Scientific studies have focused on their ontogeny, biomechanics and ecology, among other subjects. Soft tissue, both fossilized and intact, has been reported from one specimen of Tyrannosaurus rex.
...
Wikipedia
