Transverse myelitis
| Transverse myelitis | |
|---|---|
 |
|
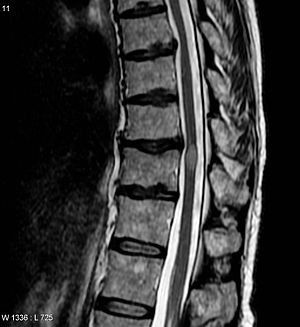
| An MRI showing a transverse myelitis lesion (the lesion is the lighter, oval shape at center-right), this MRI was taken 3 months after patient recovered | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| ICD-10 | G37.3 |
| ICD-9-CM | 323.82, 341.2 |
| DiseasesDB | 13265 |
| MeSH | D009188 |
Transverse myelitis is a neurological condition in which the spinal cord is inflamed. The inflammation damages nerve fibers, and causes them to lose their myelin coating leading to decreased electrical conductivity in the central nervous system. Transverse implies that the inflammation extends across the entire width of the spinal cord. Partial transverse myelitis and partial myelitis are terms used to define inflammation of the spinal cord that affects part of the width of the spinal cord.
There are disturbances in sensory nerves and motor nerves and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system at the level of the lesion or below. Therefore, the signs and symptoms depend on the area of spine involved:
Symptoms include weakness and numbness of the limbs, deficits in sensation and motor skills, dysfunctional sphincter activities, and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Symptoms typically develop over the course of hours or days and may progress after weeks. Sensory symptoms of transverse myelitis may include a sensation of pins and needles traveling up from the feet. Back pain can occur at the level of the inflamed segment of the spinal cord. The degree and type of sensory loss will depend upon the extent of the involvement of the various sensory tracts, but there is often a "sensory level" (at the sensory segmental level of the spinal cord below which sensation to pain or light touch is impaired). Motor weakness occurs due to involvement of the pyramidal tracts and mainly affects the muscles that flex the legs and extend the arms. Involvement of the autonomic nervous system is common and frequently leads to impaired function of the bladder and bowel and can also lead to episodes of high blood pressure.
...
Wikipedia
