Tooth socket
| Dental alveolus | |
|---|---|
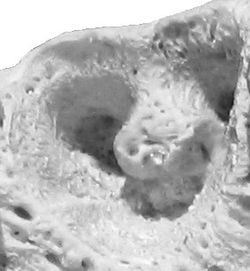
Alveola of the second premolar tooth in a bovine maxillary bone.
|
|
| Details | |
| Artery | Anterior superior alveolar arteries, Posterior superior alveolar artery, Inferior alveolar artery |
| Nerve | Anterior superior alveolar nerve, Posterior superior alveolar nerve, Inferior alveolar nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | alveolus dentalis |
| MeSH | A02.835.232.781.324.502.125.800 |
| Dorlands /Elsevier |
a_27/12123723 |
| TA |
A05.1.03.074 A03.1.03.008 |
| FMA | 57490 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
Dental alveoli (singular alveolus) are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called gomphosis (plural gomphoses). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets.
In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible.
Socket preservation or alveolar ridge preservation (ARP) is a procedure to reduce bone loss after tooth extraction to preserve the dental alveolus (tooth socket) in the alveolar bone. A platelet rich fibrin (PRF) membrane containing bone growth enhancing elements can be stitched over the wound or a graft material or scaffold is placed in the socket of an extracted tooth. The socket is then directly closed with stitches or covered with a non-resorbable or resorbable membrane and sutured.
The swelling of the dental alveoli can result in alveolitis, causing pain and discomfort to the mouth.
...
Wikipedia
