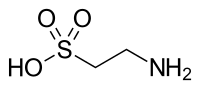
Taurine
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
2-Aminoethane-1-sulfonic acid
|
|
| Other names
2-Aminoethanesulfonic acid
Tauric acid |
|
| Identifiers | |
|
107-35-7 |
|
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:15891 |
| ChEMBL |
ChEMBL239243 |
| ChemSpider |
1091 |
| DrugBank |
DB01956 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.168 |
| 2379 | |
| PubChem | 1123 |
| UNII |
1EQV5MLY3D |
|
|
|
|
| Properties | |
| C2H7NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 125.14 g/mol |
| Density | 1.734 g/cm3 (at −173.15 °C) |
| Melting point | 305.11 °C (581.20 °F; 578.26 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | <0, 9.06 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
|
|
|
| Infobox references | |
Taurine (/ˈtɔːriːn/), or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is an organic compound that is widely distributed in animal tissues. It is a major constituent of bile and can be found in the large intestine, and accounts for up to 0.1% of total human body weight. Taurine has many fundamental biological roles, such as conjugation of bile acids, antioxidation, osmoregulation, membrane stabilization, and modulation of calcium signaling. It is essential for cardiovascular function, and development and function of skeletal muscle, the retina, and the central nervous system. Taurine is unusual among biological molecules in being a sulfonic acid, while the vast majority of biologically occurring acids contain the more weakly acidic carboxyl group. While taurine is sometimes called an amino acid, and indeed is an acid containing an amino group, it is not an amino acid in the usual biochemical meaning of the term, which refers to compounds containing both an amino and a carboxyl group.
Taurine is named after the Latin taurus (a cognate of the Greek ταῦρος) which means bull or ox, as it was first isolated from ox bile in 1827 by German scientists Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin.
...
Wikipedia
