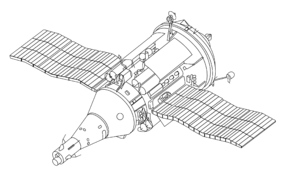
TKS spacecraft
 |
||
|---|---|---|
| Description | ||
| Role: | Manned spacecraft to supply the military Almaz space station | |
| Crew: | three | |
| Dimensions | ||
| Height: | 13.2 m | 43.31 ft |
| Diameter: | 4.15 m | 13.61 ft |
| Volume: | 45.00 m3 | |
| Rocket engines | ||
| Main Engine (N2O4/UDMH): | 7840 N | 1763 lbf ea |
| Performance | ||
| Endurance: | 7 days | |
| Apogee: | 266 km | |
| Perigee: | 223 km | |
| Inclination: | 52 degrees | |
| Spacecraft delta v: | 700 m/s | 2290 ft/s |
| Cutaway of TKS vehicle | ||
 |
||
The TKS spacecraft (Russian: Транспортный корабль снабжения, Transportnyi Korabl’ Snabzheniia, Transport Supply Spacecraft,GRAU index 11F72) was a Soviet spacecraft conceived in the late 1960s for resupply flights to the military Almaz space station.
The spacecraft was designed for both crewed and autonomous uncrewed cargo resupply flights, but was never used operationally in its intended role – only four test missions were flown (including three that docked to Salyut space stations) during the program. The Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the TKS spacecraft later formed the basis of several space station modules, including the Zarya FGB module on the International Space Station.
The TKS spacecraft consisted of two spacecraft mated together, both of which could operate independently:
While the VA carried the reentry hardware, and only minimal life support and maneuvering systems, the FGB would have been used as the primary orbital maneuvering system and cargo storage for the TKS spacecraft.
The FGB could also be used alone as an unmanned cargo module without an VA spacecraft, which enabled the FGB design to be re-purposed as FGB space station modules later on. The VA spacecraft on the other hand was also intended to be launched as "Almaz APOS", mated with an Almaz-OPS space station core as the primary orbital maneuvering system, instead of a FGB. As of August 2009[update], Excalibur Almaz planned to use the VA capsule as low-cost cargo return vehicles.
The TKS spacecraft was designed by Vladimir Chelomei (the VA capsule) and V. N. Bugayskiy (the FGB block) as a manned spacecraft launched with Proton rocket alternative to the Soyuz spacecraft for use with Almaz space stations. Development began in 1965; the Almaz programme had been abandoned by the time the first TKS spacecraft flew in 1977. The VA spacecraft ("Vozvrashaemiy Apparat") was flown separately on four test missions with two craft per launch to test the design, as well as one "all-up" test mission and three resupply missions.
...
Wikipedia
