T-cell
| T cell | |
|---|---|

Scanning electron micrograph of a human T cell
|
|
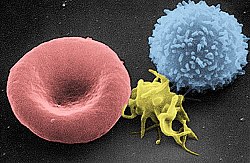
Scanning electron micrograph of T lymphocyte (right), a platelet (center) and a red blood cell (left)
|
|
| Details | |
| System | Immune system |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lymphocytus T |
| Code | TH H2.00.04.1.02007 |
|
Anatomical terminology
[]
|
|
A T cell, or T lymphocyte, is a type of lymphocyte (a subtype of white blood cell) that plays a central role in cell-mediated immunity. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells, by the presence of a T-cell receptor on the cell surface. They are called T cells because they mature in the thymus from thymocytes (although some also mature in the tonsils). The several subsets of T cells each have a distinct function. The majority of human T cells rearrange their alpha and beta chains on the cell receptor and are termed alpha beta T cells (αβ T cells) and are part of the adaptive immune system. Specialized gamma delta T cells, (a small minority of T cells in the human body, more frequent in ruminants), have invariant T-cell receptors with limited diversity, that can effectively present antigens to other T cells and are considered to be part of the innate immune system.
The category of effector T cell is a broad one that includes various T cell types that actively respond to a stimulus, such as co-stimulation. This includes helper, killer, regulatory, and potentially other T cell types.
T helper cells (TH cells) assist other white blood cells in immunologic processes, including maturation of B cells into plasma cells and memory B cells, and activation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophages. These cells are also known as CD4+ T cells because they express the CD4 glycoprotein on their surfaces. Helper T cells become activated when they are presented with peptide antigens by MHC class II molecules, which are expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Once activated, they divide rapidly and secrete small proteins called cytokines that regulate or assist in the active immune response. These cells can differentiate into one of several subtypes, including TH1, TH2, TH3, TH17, TH9, or TFH, which secrete different cytokines to facilitate different types of immune responses. Signalling from the APC directs T cells into particular subtypes.
...
Wikipedia
