Supraspinatus
| Supraspinatus muscle | |
|---|---|
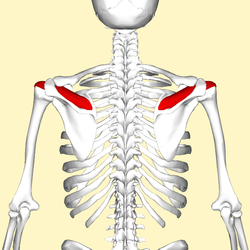
Position of the supraspinatus muscle (red) seen from the back.
|
|

Posterior view of muscles connecting the upper extremity to the vertebral column. Supraspinatus muscle is labeled in red at right, while it is covered by other muscles at left.
|
|
| Details | |
| Origin | supraspinous fossa of scapula |
| Insertion | superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus |
| Artery | suprascapular artery |
| Nerve | suprascapular nerve |
| Actions | abduction of arm and stabilizes humerus see part on controversy of action. |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus supraspinatus |
| TA | A04.6.02.006 |
| FMA | 9629 |
|
Anatomical terms of muscle
[]
|
|
The supraspinatus (plural supraspinati, from Latin supraspinatus) is a relatively small muscle of the upper back that runs from the supraspinatous fossa superior portion of the scapula (shoulder blade) to the greater tubercle of the humerus. It is one of the four rotator cuff muscles and also abducts the arm at the shoulder. The spine of the scapula separates the supraspinatus muscle from the infraspinatus muscle, which originates below the spine.
The supraspinatus muscle arises from the supraspinous fossa, a shallow depression in the body of the scapula above its spine. The supraspinatus muscle tendon passes laterally beneath the cover of the acromion. Research in 1996 showed that the postero-lateral origin was more lateral than classically described.
The supraspinatus tendon is inserted into the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The distal attachments of the three rotator cuff muscles that insert into the greater tubercle of the humerus can be abbreviated as SIT when viewed from superior to inferior (for supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor), or SITS when the subscapularis muscle, which attaches to the lesser tubercle of the humerus, is included.
The suprascapular nerve (C5)innervates the supraspinatus muscle as well as the infraspinatus muscle. It comes from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. This nerve can be damaged along its course in fractures of the overlying clavicle, which can reduce the person's ability to initiate the abduction.
...
Wikipedia
